
1 day ago

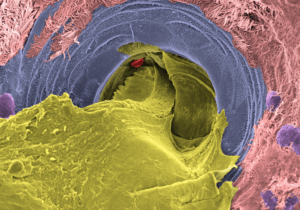
Above is a highly magnified image showing the inside of a mucus-producing gland in the airway of a person with cystic fibrosis taken with a scanning electron microscope. The gland opening is occupied by thick mucus. The airway tissue was collected from a donated lung during transplant surgery and then treated with a compound that stimulates gland secretion before the image was taken. The picture was later colored on a computer to help show the different parts: mucus is yellow, ciliated cells – the tiny hair-like structures that normally help move mucus – are pink, the gland opening is blue, mucus-producing cells are purple, and a red blood cell that fell in the gland opening is shown in red.
This image was provided by the Ehre Lab: Camille Ehre, PhD | Marsico Lung Institute

1 day ago

3 weeks ago

1 month ago

1 month ago